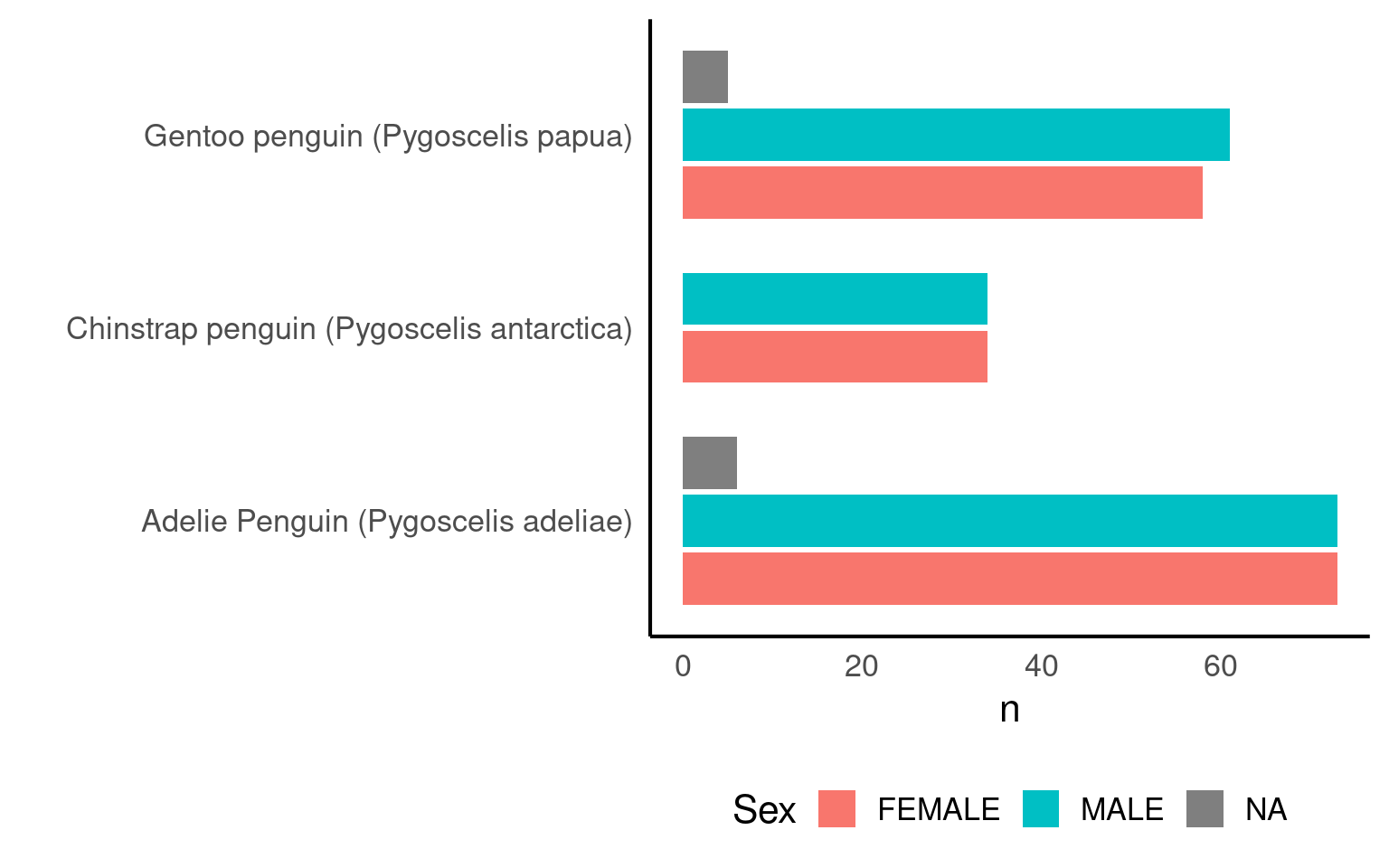Rows: 344
Columns: 17
$ studyName <chr> "PAL0708", "PAL0708", "PAL0708", "PAL0708", "PAL…
$ `Sample Number` <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1…
$ Species <chr> "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)", "Adelie P…
$ Region <chr> "Anvers", "Anvers", "Anvers", "Anvers", "Anvers"…
$ Island <chr> "Torgersen", "Torgersen", "Torgersen", "Torgerse…
$ Stage <chr> "Adult, 1 Egg Stage", "Adult, 1 Egg Stage", "Adu…
$ `Individual ID` <chr> "N1A1", "N1A2", "N2A1", "N2A2", "N3A1", "N3A2", …
$ `Clutch Completion` <chr> "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "Yes", "No", …
$ `Date Egg` <chr> "11/11/2007", "11/11/2007", "16/11/2007", "16/11…
$ `Culmen Length (mm)` <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, 36.7, 39.3, 38.9, 39.2, 34…
$ `Culmen Depth (mm)` <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, 19.3, 20.6, 17.8, 19.6, 18…
$ `Flipper Length (mm)` <dbl> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193, 190, 181, 195, 193, 190,…
$ `Body Mass (g)` <dbl> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, 3450, 3650, 3625, 4675, 34…
$ Sex <chr> "MALE", "FEMALE", "FEMALE", NA, "FEMALE", "MALE"…
$ `Delta 15 N (o/oo)` <dbl> NA, 8.94956, 8.36821, NA, 8.76651, 8.66496, 9.18…
$ `Delta 13 C (o/oo)` <dbl> NA, -24.69454, -25.33302, NA, -25.32426, -25.298…
$ Comments <chr> "Not enough blood for isotopes.", NA, NA, "Adult…6 Summarise
6.1 Learning Objectives
Use summary functions to explore the structure and completeness of a dataset.
Create simple summaries and grouped summaries using
count(),group_by(), andsummarise().Calculate descriptive statistics (mean, SD) across groups.
Use
janitortools Firke (2024) to quickly tabulate and summarise categorical data.
6.2 A first glimpse
When starting with a new dataset, we want to get an initial idea:
How many rows and columns are there?
What are the column names?
What types of data are in each column?
What are their possible values or ranges?
These answers are useful to know before jumping into wrangling and cleaning data.
There are several ways to return an overview of your data, ranging in how comprehensively you wish to summarise your data’s structure.
spc_tbl_ [344 × 17] (S3: spec_tbl_df/tbl_df/tbl/data.frame)
$ studyName : chr [1:344] "PAL0708" "PAL0708" "PAL0708" "PAL0708" ...
$ Sample Number : num [1:344] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
$ Species : chr [1:344] "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)" "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)" "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)" "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)" ...
$ Region : chr [1:344] "Anvers" "Anvers" "Anvers" "Anvers" ...
$ Island : chr [1:344] "Torgersen" "Torgersen" "Torgersen" "Torgersen" ...
$ Stage : chr [1:344] "Adult, 1 Egg Stage" "Adult, 1 Egg Stage" "Adult, 1 Egg Stage" "Adult, 1 Egg Stage" ...
$ Individual ID : chr [1:344] "N1A1" "N1A2" "N2A1" "N2A2" ...
$ Clutch Completion : chr [1:344] "Yes" "Yes" "Yes" "Yes" ...
$ Date Egg : chr [1:344] "11/11/2007" "11/11/2007" "16/11/2007" "16/11/2007" ...
$ Culmen Length (mm) : num [1:344] 39.1 39.5 40.3 NA 36.7 39.3 38.9 39.2 34.1 42 ...
$ Culmen Depth (mm) : num [1:344] 18.7 17.4 18 NA 19.3 20.6 17.8 19.6 18.1 20.2 ...
$ Flipper Length (mm): num [1:344] 181 186 195 NA 193 190 181 195 193 190 ...
$ Body Mass (g) : num [1:344] 3750 3800 3250 NA 3450 ...
$ Sex : chr [1:344] "MALE" "FEMALE" "FEMALE" NA ...
$ Delta 15 N (o/oo) : num [1:344] NA 8.95 8.37 NA 8.77 ...
$ Delta 13 C (o/oo) : num [1:344] NA -24.7 -25.3 NA -25.3 ...
$ Comments : chr [1:344] "Not enough blood for isotopes." NA NA "Adult not sampled." ...
- attr(*, "spec")=
.. cols(
.. studyName = col_character(),
.. `Sample Number` = col_double(),
.. Species = col_character(),
.. Region = col_character(),
.. Island = col_character(),
.. Stage = col_character(),
.. `Individual ID` = col_character(),
.. `Clutch Completion` = col_character(),
.. `Date Egg` = col_character(),
.. `Culmen Length (mm)` = col_double(),
.. `Culmen Depth (mm)` = col_double(),
.. `Flipper Length (mm)` = col_double(),
.. `Body Mass (g)` = col_double(),
.. Sex = col_character(),
.. `Delta 15 N (o/oo)` = col_double(),
.. `Delta 13 C (o/oo)` = col_double(),
.. Comments = col_character()
.. )
- attr(*, "problems")=<externalptr> | Name | penguins_raw |
| Number of rows | 344 |
| Number of columns | 17 |
| _______________________ | |
| Column type frequency: | |
| character | 10 |
| numeric | 7 |
| ________________________ | |
| Group variables | None |
Variable type: character
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | empty | n_unique | whitespace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| studyName | 0 | 1.00 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Species | 0 | 1.00 | 33 | 41 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Region | 0 | 1.00 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Island | 0 | 1.00 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| Stage | 0 | 1.00 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Individual ID | 0 | 1.00 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 190 | 0 |
| Clutch Completion | 0 | 1.00 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Date Egg | 0 | 1.00 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 50 | 0 |
| Sex | 11 | 0.97 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Comments | 290 | 0.16 | 18 | 68 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
Variable type: numeric
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | mean | sd | p0 | p25 | p50 | p75 | p100 | hist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Number | 0 | 1.00 | 63.15 | 40.43 | 1.00 | 29.00 | 58.00 | 95.25 | 152.00 | ▇▇▆▅▃ |
| Culmen Length (mm) | 2 | 0.99 | 43.92 | 5.46 | 32.10 | 39.23 | 44.45 | 48.50 | 59.60 | ▃▇▇▆▁ |
| Culmen Depth (mm) | 2 | 0.99 | 17.15 | 1.97 | 13.10 | 15.60 | 17.30 | 18.70 | 21.50 | ▅▅▇▇▂ |
| Flipper Length (mm) | 2 | 0.99 | 200.92 | 14.06 | 172.00 | 190.00 | 197.00 | 213.00 | 231.00 | ▂▇▃▅▂ |
| Body Mass (g) | 2 | 0.99 | 4201.75 | 801.95 | 2700.00 | 3550.00 | 4050.00 | 4750.00 | 6300.00 | ▃▇▆▃▂ |
| Delta 15 N (o/oo) | 14 | 0.96 | 8.73 | 0.55 | 7.63 | 8.30 | 8.65 | 9.17 | 10.03 | ▃▇▆▅▂ |
| Delta 13 C (o/oo) | 13 | 0.96 | -25.69 | 0.79 | -27.02 | -26.32 | -25.83 | -25.06 | -23.79 | ▆▇▅▅▂ |
At this early stage, it’s helpful to assess whether your dataset meets your expectations. Consider if the data appear as anticipated. Are the values in each column reasonable? Are there any noticeable gaps or errors that might need to be corrected, or that could potentially render the data unusable?
Your turn
The dataset has rows (including the headers) and 17 columns.
It also provides information on the type of data in each column
<chr>- means character or text data<dbl>- means numerical data
Q Based on our summary functions are any variables assigned to the wrong data type (should be character when numeric or vice versa)?
Although some columns like date might not be correctly treated as character variables, they are not strictly numeric either, all other columns appear correct
Q Based on our summary functions do we have complete data for all variables?
No, they are 2 missing data points for body measurements (culmen, flipper, body mass), 11 missing data points for sex, 13/14 missing data points for blood isotopes (Delta N/C) and 290 missing data points for comments
We have just learned some ways to initially inspect our dataset. Keep in mind, we don’t expect everything to be perfect. This initial inspection is a good opportunity to identify where these issues might be and assess their severity.
When you are confident that the dataset is largely as expected, you are ready to start summarising your data.
6.3 Summary counts
In the previous section, we learned how to get an overview of our data’s structure, including the number of rows, the columns present, and any missing data. In this section, we will focus on summarising the data. Summarising data can provide insight into the scope and variation in our dataset, and help in evaluating its suitability for our analysis.
With our data we can count the total number of occurrences for different groups either by:
6.3.1 Filtering
6.3.2 Grouping
Or by grouping :
6.4 Frequency counts by subgroups
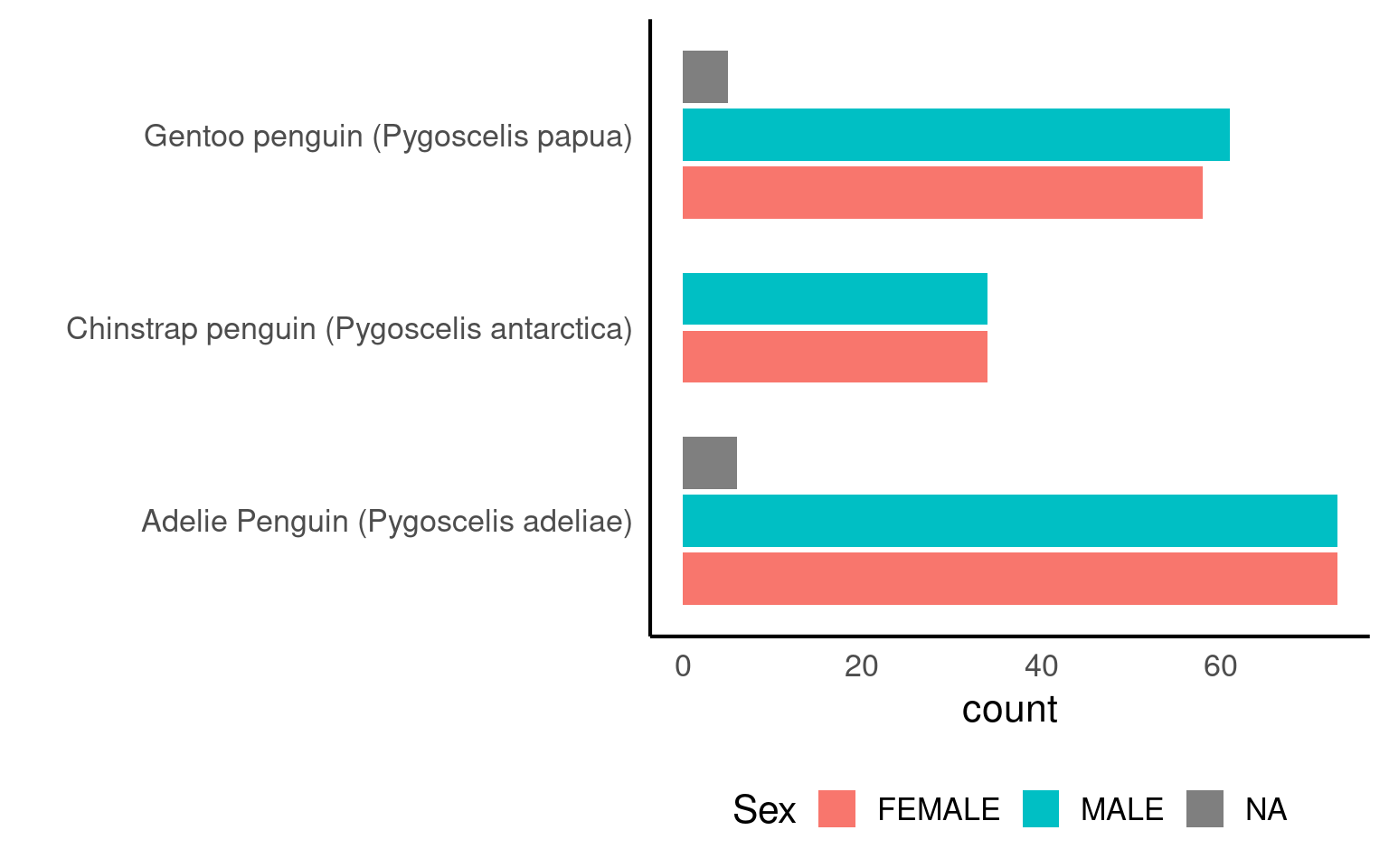
We can apply multiple grouping parameters at the same time - for example if we wish to know the frequency of observations by species and sex.
We can do this using dplyr or with functions in the janitor package:
| Species | Sex | n |
|---|---|---|
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | FEMALE | 73 |
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | MALE | 73 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | MALE | 61 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | FEMALE | 58 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | FEMALE | 34 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | MALE | 34 |
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | NA | 6 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | NA | 5 |
| Sex | Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEMALE | 21.2% | 9.9% | 16.9% | 48.0% |
| MALE | 21.2% | 9.9% | 17.7% | 48.8% |
| NA | 1.7% | 0.0% | 1.5% | 3.2% |
| Total | 44.2% | 19.8% | 36.0% | 100.0% |
6.5 Visualising Frequencies
Graphs make summaries easier to interpret at a glance.
6.6 Summary statistics
We can extend our summaries to show not just counts, but also measures of central tendency (mean) and spread (standard deviation).
These are powerful ways to understand variation within groups.
| Species | mean_mass | sd_mass | n |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | 3700.662 | 458.5661 | 152 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | 3733.088 | 384.3351 | 68 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | 5076.016 | 504.1162 | 124 |
Your turn
| Species | Sex | mean_mass_g | sd_mass_g | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | FEMALE | 3368.836 | 269.3801 | 73 |
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | MALE | 4043.493 | 346.8116 | 73 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | FEMALE | 3527.206 | 285.3339 | 34 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | MALE | 3938.971 | 362.1376 | 34 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | FEMALE | 4679.741 | 281.5783 | 58 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | MALE | 5484.836 | 313.1586 | 61 |
6.6.1 Summarise multiple variables
summarise_at()
Summarise specific selected variables:
| Species | Flipper Length (mm) | Culmen Length (mm) | Culmen Depth (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | 189.9536 | 38.79139 | 18.34636 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | 195.8235 | 48.83382 | 18.42059 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | 217.1870 | 47.50488 | 14.98211 |
summarise_if()
| Species | Sample Number | Culmen Length (mm) | Culmen Depth (mm) | Flipper Length (mm) | Body Mass (g) | Delta 15 N (o/oo) | Delta 13 C (o/oo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae) | 76.5 | 38.79139 | 18.34636 | 189.9536 | 3700.662 | 8.859733 | -25.80419 |
| Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) | 34.5 | 48.83382 | 18.42059 | 195.8235 | 3733.088 | 9.356155 | -24.54654 |
| Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua) | 62.5 | 47.50488 | 14.98211 | 217.1870 | 5076.016 | 8.245338 | -26.18530 |
6.6.2 Useful summary functions
6.6.2.1 Measure of location:
mean(x): sum of x divided by the length
median(x): 50% of x is above and 50% is below
6.6.2.2 Measure of variation:
sd(x): standard deviation
IQR(x): interquartile range (robust equivalent of sd when outliers are present in the data)
6.6.2.3 Measure of rank:
min(x): minimum value of x
max(x): maximum value of x
quantile(x, 0.25): 25% of x is below this value
6.6.2.4 Counts:
n(x): the number of element in x
sum(!is.na(x)): count non-missing values
n_distinct(x): count the number of unique value
6.7 Summary
In this section we learned to:
-
Inspect structure and completeness
Use
glimpse(),str(), andskim()to understand column types, missing data, and variable ranges.Confirm that variables are stored in appropriate formats (e.g. numeric vs character).
-
Summarise counts and categories
Count observations using
count()andgroup_by()to explore dataset composition.Use
janitor::tabyl()for fast, readable cross-tabulations and percentages. -
Calculate descriptive statistics
- Compute group-wise summaries with
summarise()such as means, SDs, and counts.
- Compute group-wise summaries with