#___________________________----
# SET UP ----
# An analysis of the bill dimensions of male and female
# Adelie, Gentoo and Chinstrap penguins
# Data first published in Gorman, KB, TD Williams, and WR Fraser.
# 2014.
# “Ecological Sexual Dimorphism and Environmental Variability
# Within a Community of Antarctic Penguins (Genus Pygoscelis).”
# PLos One 9 (3): e90081.
# https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090081.
#__________________________----
# PACKAGES ----
library(tidyverse) # tidy data packages
library(here) # organised file paths
library(janitor) # cleans variable names
#__________________________----
# IMPORT DATA ----
penguins_raw <- read_csv(here("data", "raw", "penguins_raw.csv"))
# check the data has loaded, prints first 10 rows of dataframe
penguins_raw
#__________________________----
# CLEAN DATA ----
# clean all variable names to snake_case
# using the clean_names function from the janitor package
# note we are using assign <-
# to overwrite the old version of penguins
# with a version that has updated names
# this changes the data in our R workspace
# but NOT the original csv file
# clean the column names
# assign to new R object
penguins_clean_names <- janitor::clean_names(penguins_raw)
# quickly check the new variable names
colnames(penguins_clean_names)
# shorten the variable names for N and C isotope blood samples
penguins_clean_names <- rename(penguins_clean_names,
"delta_15n"="delta_15_n_o_oo", # use rename from the dplyr package
"delta_13c"="delta_13_c_o_oo")
# use mutate and case_when for a statement that conditionally changes the names of the values in a variable
penguins <- penguins_clean_names |>
mutate(species = case_when(species == "Adelie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae)" ~ "Adelie",
species == "Gentoo penguin (Pygoscelis papua)" ~ "Gentoo",
species == "Chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica)" ~ "Chinstrap"))
# use mutate and if_else
# for a statement that conditionally changes
# the names of the values in a variable
penguins <- penguins |>
mutate(sex = if_else(
sex == "MALE", "Male", "Female"
)
)
# use lubridate to format date and extract the year
penguins <- penguins |>
mutate(date_egg = lubridate::dmy(date_egg))
penguins <- penguins |>
mutate(year = lubridate::year(date_egg))
# Set body mass ranges
penguins <- penguins |>
mutate(mass_range = case_when(
body_mass_g <= 3500 ~ "smol penguin",
body_mass_g >3500 & body_mass_g < 4500 ~ "mid penguin",
body_mass_g >= 4500 ~ "chonk penguin",
.default = NA)
)
# Assign these to an ordered factor
penguins <- penguins |>
mutate(mass_range = fct_relevel(mass_range,
"smol penguin",
"mid penguin",
"chonk penguin")
)
# WRITE CLEAN DATA ----
## Optional ----
write_csv(penguins, here::here("data", "clean", "penguins_clean.csv"))14 Scripts
14.0.1 Save scripts
- Make sure you have saved your script 💾 and given it the filename
01_import_penguins_data.Rit should be saved in your scripts folder
- Does your workspace look like the below?
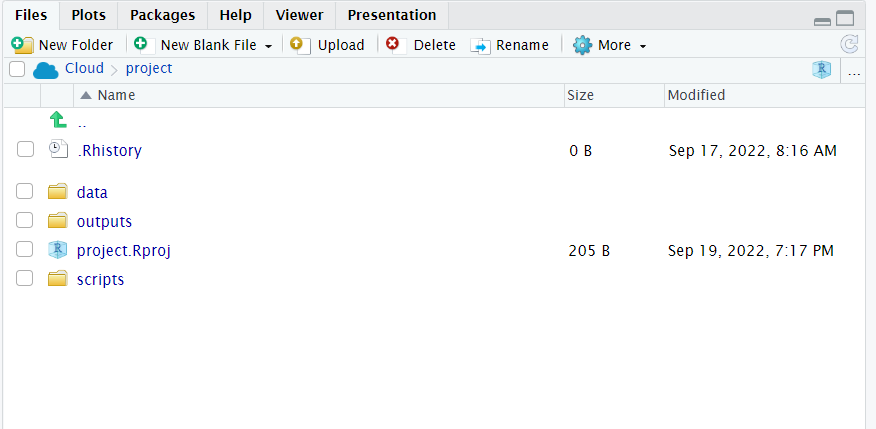
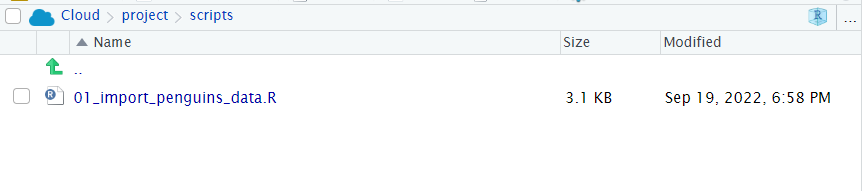
- Does your script run from a
blank slatewithout errors?
14.0.2 Checklist for data checking
Is our dataframe in a tidy format?
-
Is each column assigned to the correct data type?
- Are dates formatted correctly?
- Are factors set where needed, are the levels in the correct order?
Are variables consistently named (e.g. using a naming convention such as snake_case)?
Are text values in an appropriate format?
Do we have any data duplication?
Are there any typos or mistakes in character strings?
14.1 Running a script from console
Now that we have made an import and cleaning script, we can check our blank slates set-up and that our script runs without errors:
14.2 Essential shortcuts
-
Comment/uncomment -
Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + c- Highlight text and use shortcut keys to commment out text
-
Rename in scope -
Ctrl/Cmd + Alt + Shift + M- Highlight an R object then use this shortcut key to rename all examples in the script
14.3 Layout
Define logical regions of scripts with either
----or====after#This uses markdown logic, #, ##, ### to define titles, headers and subheaders
Use
stylerto help format code and keep it neat